Configure STP mode PVST on a Cisco Switch
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) prevents network loops in a Layer 2 switching environment by selectively blocking redundant paths. In this article, we configure the Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) mode on Cisco switches using a three-switch topology. PVST allows a separate STP instance for each VLAN, enabling more granular control of traffic flow in VLAN-based networks.
STP
- Configure STP mode PVST on a Cisco Switch
- Configure STP mode Rapid PVST on a Cisco Switch
- Configure STP mode Rapid PVST with PortFast on a Cisco Switch
Topology
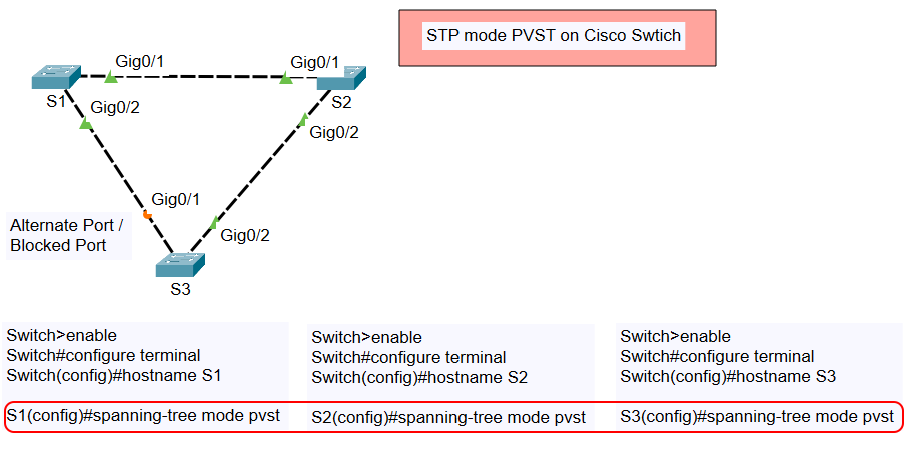
The topology consists of three Cisco switches, S1, S2, and S3, interconnected as shown below:
- S1 is connected to S2 via GigabitEthernet 0/1.
- S1 is connected to S3 via GigabitEthernet 0/2.
- S2 is connected to S3 via GigabitEthernet 0/1.
In this configuration:
- STP will block one redundant port to prevent network loops.
- The topology ensures high availability by automatically reactivating the blocked port if an active link fails.
Configuration Steps
- Set the Hostnames
Assign descriptive hostnames to each switch to make network management easier.Repeat the same steps for the other two switches, replacing
S1withS2andS3. - Enable PVST Mode
Configure each switch to operate in PVST mode. PVST provides one STP instance per VLAN, optimizing the path selection process.
For S1:For S2:
For S3:
- Verify and Monitor STP
Use the following commands to verify the STP configuration and monitor the status of the ports:This command displays information about the root bridge, blocked ports, and active ports. Confirm that one of the redundant links is in the blocking state, ensuring no loops occur in the network.
Example Output
After configuration, you should see:
- One port in the blocking state to prevent loops (e.g., Gig0/1 on S3).
- The remaining ports in the forwarding state.
Conclusion
Configuring PVST mode on Cisco switches ensures loop-free and efficient VLAN-based network traffic. By following the steps outlined above, you can set up a reliable and robust spanning-tree topology.
Next Steps
Explore advanced STP configurations like Rapid PVST+ or MSTP for more complex network environments.